The speed at which white glue can be dispensed using robotic systems depends on several key factors, including the properties of the glue, the type of dispensing mechanism, the robotic platform, and the application requirements. Below is a detailed analysis of these factors and typical performance characteristics:
1. Glue Characteristics
-
Viscosity: White glue (commonly polyvinyl acetate, PVA) typically has a medium viscosity, often ranging from 2,000 to 20,000 centipoise (cP) depending on formulation and temperature. Higher viscosity glues require more pressure or slower dispensing speeds to maintain a consistent bead and avoid issues like stringing or clogging.
-
Cure Time and Flow Behavior: White glue usually has a slow cure time and is water-based; careful speed regulation is necessary to ensure proper application without excessive spreading.
2. Dispensing Mechanism Types
-
Needle or Nozzle Size: Smaller orifice sizes (e.g., 0.2–0.8 mm) result in finer glue beads but may reduce maximum flow rate.
-
Valve Type:
-
Needle valves: Enable precise on/off control but might limit cycle speed due to mechanical movement.
-
Diaphragm valves: Allow faster switching times, suitable for rapid dispensing.
-
Auger or piston pumps: Used for high-viscosity materials, provide consistent volumetric dispensing but may limit speed depending on pump capacity.
-
3. Robotic Platform
-
Cartesian Gantry Robots: Typically used for fast, repetitive dispensing lines; can achieve repeatability in the range of ±0.05 mm and speeds up to 800 mm/s.
-
Articulated Robots: More flexible for complex paths but may run at slower linear speeds (100–400 mm/s) to maintain precision.
-
Delta Robots: Used for ultra-fast picking and placing, sometimes adaptable for dispensing in high-speed production lines.
4. Typical Dispensing Speeds
-
Low-to-Medium Viscosity White Glue: Speeds of 200–800 mm/s are achievable.
-
At the higher end (~800 mm/s), system optimization is crucial to avoid glue stringing or inconsistent bead formation.
-
-
Cycle Time: High-performance dispensing valves can open/close within 10–20 milliseconds, enabling rapid start/stop dispensing cycles.
5. Factors Affecting Speed and Quality
-
System Pressure and Flow Rate: Adequate pressure must be maintained to keep a uniform bead without excessive globs.
-
Robot Communication Latency: Fast response times (
-
Environmental Conditions: Temperature and humidity affect glue viscosity and flow; temperature-controlled dispensing stations may be necessary.
-
Nozzle Design and Maintenance: Advanced anti-stringing nozzles and regular nozzle cleaning help maintain high-speed dispensing quality.
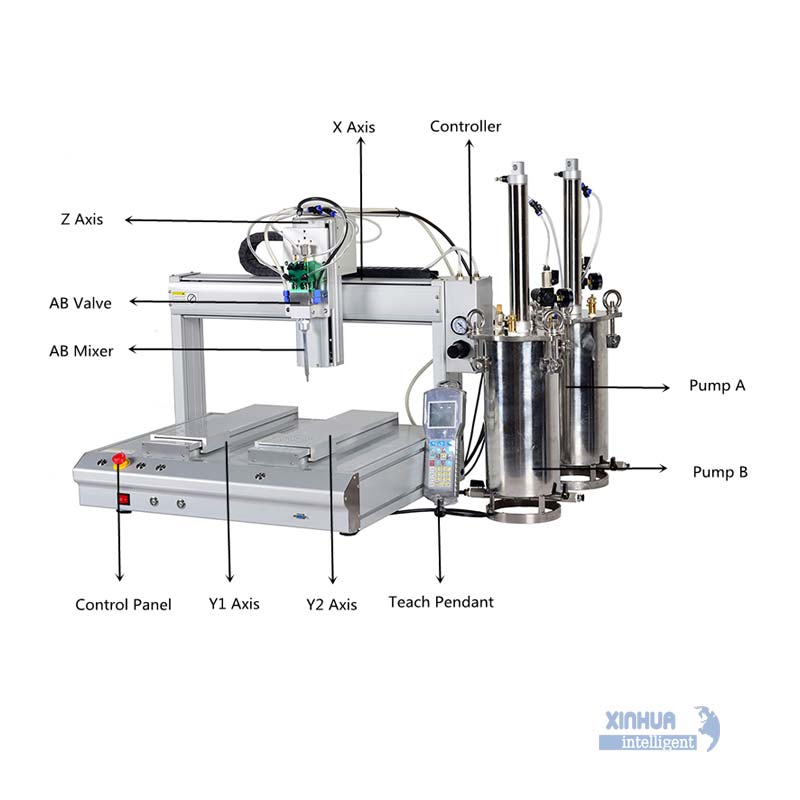
Summary
| Parameter | Typical Range/Value |
|---|---|
| Glue Viscosity | 2,000 – 20,000 cP |
| Robotic Linear Speed | 200 – 800 mm/s |
| Valve Open/Close Speed | 10 – 20 ms |
| Typical Bead Diameter | 0.2 – 2 mm (depending on nozzle) |
| Repeatability | ±0.05 mm (Cartesian robots) |
Conclusion
Industrial robotic dispensing systems can reliably dispense white glue at speeds up to approximately 800 mm/s, provided system parameters such as glue viscosity, valve type, nozzle design, and robot control cycle times are optimized. Achieving these high speeds without compromising bead consistency requires well-maintained equipment and possibly environmental controls.
If you require information for a specific robotic dispenser model or glue type, consulting the manufacturer’s technical data is recommended for precise speed and flow rate specifications.
